Fine for Non Filing of GST Return
Understanding the Consequences: Fine for Non-Filing of GST Returns in India
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, implemented in India in July 2017, has streamlined the taxation system and brought about significant changes in the way businesses manage their taxes. Under GST, businesses are required to file regular returns to report their sales, purchases, and tax liabilities. Failure to comply with GST return filing obligations can result in penalties and fines. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the details of the fines and penalties for non-filing of GST returns in India.
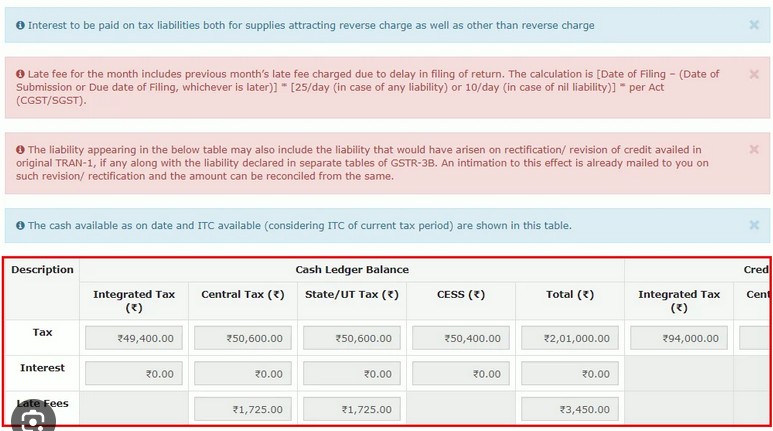
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Background of GST in India
- Importance of GST Return Filing
- Types of GST Returns
- GSTR-1: Outward Supplies
- GSTR-3B: Summary Return
- GSTR-9: Annual Return
- GST Return Due Dates
- Monthly and Quarterly Filing
- Due Dates for Different Returns
- Penalties for Non-Filing
- Late Filing Fee
- Interest on Tax Liability
- Penalty for Non-Filing
- Reasons for Non-Filing
- Common Causes
- Challenges Faced by Businesses
- Impact of Non-Filing
- Legal Consequences
- Blocked Input Tax Credit
- Fine Calculation
- Late Fee Calculation
- Interest Calculation
- Compliance and Avoidance
- Importance of Timely Filing
- Filing Process Simplification
- Case Studies
- Real-Life Examples of Non-Filing Cases
- FAQs
- Answers to Common Questions
- Conclusion
- Summary of Key Points
1. Introduction
Background of GST in India
GST, often referred to as the “one nation, one tax” system, was introduced in India to replace a complex web of indirect taxes, such as Value Added Tax (VAT), Central Excise Duty, and Service Tax. This unified tax system aimed to simplify tax compliance, reduce tax evasion, and create a seamless national market.
Importance of GST Return Filing
Under the GST regime, registered taxpayers are required to file various GST returns, depending on their type of business and turnover. GST returns are the primary means by which businesses report their sales, purchases, and the tax liability they have accrued. Timely and accurate filing of GST returns is essential not only for compliance but also for ensuring a smooth flow of input tax credit.
2. Types of GST Returns
There are several types of GST returns that businesses may be required to file. Here are three key types:
GSTR-1: Outward Supplies
GSTR-1 is a monthly or quarterly return that contains details of all outward supplies made by the registered taxpayer. It includes information on sales invoices, credit and debit notes, and advances received.
GSTR-3B: Summary Return
GSTR-3B is a monthly return that summarizes the details of outward and inward supplies, along with the tax liability. It is a self-declaration of taxes payable and tax credits available.
GSTR-9: Annual Return
GSTR-9 is an annual return that consolidates the monthly or quarterly returns filed during the financial year. It provides a comprehensive view of the taxpayer’s activities for the year.
3. GST Return Due Dates
GST return due dates vary depending on the type of return and the turnover of the taxpayer. For instance, taxpayers with a turnover of less than ₹1.5 crore have the option to file GSTR-1 on a quarterly basis, while those with higher turnover must file it monthly. GSTR-3B is generally due on the 20th of the following month.
4. Penalties for Non-Filing
Late Filing Fee
The late filing of GST returns attracts a late fee. As of the latest GST provisions, the late fee is ₹50 per day for Central GST (CGST) and ₹50 per day for State GST (SGST). Therefore, the total late fee is ₹100 per day of delay.
Interest on Tax Liability
In addition to the late fee, businesses are also liable to pay interest on the outstanding tax liability. The interest rate is 18% per annum, calculated on the outstanding tax amount.
Penalty for Non-Filing
Apart from late fees and interest, businesses that fail to file their GST returns are subject to a penalty. The penalty is a hefty ₹10,000 or 10% of the tax due, whichever is higher. This penalty applies to each return that remains unfiled.
5. Reasons for Non-Filing
Common Causes
There are several reasons why businesses may fail to file their GST returns on time:
- Lack of Awareness: Some businesses, particularly smaller ones, may not be fully aware of their GST obligations or filing deadlines.
- Technical Issues: Technical glitches on the GST portal can hinder the filing process.
- Financial Constraints: Businesses facing financial difficulties may delay filing to avoid immediate tax payments.
Challenges Faced by Businesses
- Complexity: GST compliance can be complex, especially for businesses operating in multiple states or with diverse product lines.
- IT Issues: Some businesses may lack the necessary IT infrastructure to manage GST compliance effectively.
- Resource Constraints: Small and medium-sized businesses may have limited resources for dedicated tax compliance teams.
6. Impact of Non-Filing
Legal Consequences
Non-filing of GST returns can have serious legal consequences, including:
- Legal Action: The GST authorities can initiate legal proceedings against the non-compliant business.
- Cancellation of Registration: The GST registration of the business can be canceled, effectively stopping its operations.
Blocked Input Tax Credit
Non-filing can also lead to the blocking of input tax credit. When businesses do not file their returns on time, other taxpayers who have done so cannot claim input tax credit for the tax paid on their purchases from non-compliant suppliers. This can significantly affect the cash flow of both the supplier and the recipient.
7. Fine Calculation
Late Fee Calculation
The late fee for GST return filing is calculated at ₹50 per day for CGST and ₹50 per day for SGST, making it ₹100 per day of delay. The late fee is calculated from the due date of filing to the date of actual filing.
Interest Calculation
Interest on the tax liability is charged at a rate of 18% per annum, calculated on the outstanding tax amount. The interest is calculated from the due date of filing to the date of payment.
8. Compliance and Avoidance
Importance of Timely Filing
To avoid fines, penalties, and blocked input tax credit, it is crucial for businesses to file their GST returns on time. This requires a clear understanding of the GST return filing process and due dates.
Filing Process Simplification
Businesses can simplify the GST return filing process by using accounting software or engaging tax professionals. Regularly reconciling accounts and maintaining up-to-date records can also streamline the compliance process.
9. Case Studies
Let’s examine a few hypothetical case studies to illustrate the financial impact of non-filing:
Case Study 1: Late Filing
Scenario: A small retailer with a monthly turnover of ₹10 lakh fails to file their GSTR-3B return for three months consecutively.
Late Fee: ₹100 per day for each return
Interest: 18% per annum on the outstanding tax liability
Penalty: 10% of the tax due or ₹10,000, whichever is higher, for each return
Case Study 2: Cancellation of Registration
Scenario: A medium-sized manufacturer with a monthly turnover of ₹2 crore fails to file their GSTR-1 return for six consecutive months.
Consequence: Their GST registration is canceled, effectively shutting down their business operations.
10. FAQs
Q1: Can I file a belated GST return after the due date?
Yes, you can file a belated GST return, but it will attract late filing fees and interest charges. The late fee is ₹100 per day for each day of delay.
Q2: What if I made a mistake in my filed return? Can I revise it?
Yes, you can revise your GST return if you discover any errors or omissions. However, there are specific rules and time limits for doing so.
Q3: How can I ensure timely GST return filing?
To ensure timely GST return filing, consider using GST-compliant accounting software, engaging a tax consultant, and maintaining accurate financial records.
11. Conclusion
Filing GST returns on time is not only a legal requirement but also essential for maintaining a healthy cash flow and availing input tax credit. Non-filing can lead to fines, penalties, and blocked credit, adversely affecting your business. To avoid these consequences, it’s crucial to understand your GST obligations, file returns promptly, and seek professional assistance when needed. Compliance is not just a legal requirement; it’s a vital aspect of running a successful and sustainable business in the GST era.