Looking For Funding?
‘Funding’ refers to the money required to start and run a business. It is a financial investment in a company for product development, manufacturing, expansion, sales and marketing, office spaces, and inventory.
Many startups choose to not raise funding from third parties and are funded by their founders only (to prevent debts and equity dilution). However, most startups do raise funding, especially as they grow larger and scale their operations. If you are an entrepreneur seeking to understand why funding is needed, types of funding available, and how to raise funding.Get Enquirer Now
All You Need To Know About Funding
Then read on to find answers to these important questions.
1. Why is Funding Required?
A startup might require funding for one, a few, or all of the following purposes. It is important that you, as an entrepreneur, are clear about why you are raising funds. You should have a detailed financial and business plan before you approach investors.
- Prototype creation, product development, website/app development
- Team hiring
- Legal and consulting services for your startup
- Raw materials and equipment
- Licenses and certifications
- Working capital
- Marketing and Sales
- Office space and other admin expenses
2. Types of Funding

3. Stages of Startups and Sources of Funding
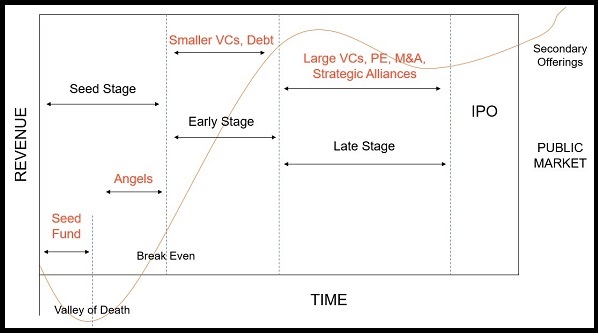
There are multiple sources of funding available for startups. However, the source of funding should typically match the stage of operations of the startup. Please note that raising funds from external sources is a time-consuming process and can easily take over 6 months to convert.
Ideation/Pre-Seed Stage
This the stage where you, the entrepreneur, has an idea and are working on bringing it to life. At this stage, the amount of funds needed is usually small.
Given the fact that you are at such an initial stage in the startup lifecycle, there are very limited and mostly informal channels available for raising funds. Common funding sources utilized by startups in this stage are:
- Bootstrapping/Self-financing: Bootstrapping a startup means growing your business with little or no venture capital or outside investment. It means relying on your own savings and revenue to operate and expand. This is the first recourse for most entrepreneurs as there is no pressure to pay back the funds or dilute control of your startup.
- Friends and Family: This is also a commonly utilized channel of funding by entrepreneurs still in the early stages. The major benefit of this source of investment is that there is an inherent level of trust between the entrepreneurs and the investors
- Business Plan/Pitching Events: This is the prize money/grants/financial benefits that is provided by institutes or organizations that conduct business plan competitions and challenges. Even though the quantum of money is not generally large, it is usually enough at idea stage. What makes the difference at these events is having a good business plan. Click Here to Access Resources
Validation/Seed Stage
This is the stage where your startup has a prototype ready and you need to validate the potential demand for your startup’s product/service. This is called conducting a ‘Proof of Concept (PoC)’, after which comes the big market launch. To do this, the startup will need to conduct field trials, test the product on a few potential customers, onboard mentors, and build a formal team. Common funding sources utilized by startups in this stage are:
- Incubators: Incubators are organizations set-up with the specific goal of assisting entrepreneurs with building and launching their startups. Not only do incubators offer a lot of value-added services (office space, utilities, admin & legal assistance, etc.), they often also make grants/debt/equity investments
- Government Loan Schemes: The government has initiated a few loan schemes to provide collateral-free debt to aspiring entrepreneurs and help them gain access to low-cost capital. Some such schemes include CGTMSE, MUDRA, and Stand-up India.
- Angel Investors: Angel investors are individuals who invest their money into high potential startups in return for equity. Reach out to angel networks such as Indian Angel Network, Mumbai Angels, Lead Angels, Chennai Angels, etc. or relevant industrialists for this.
- Crowd funding: Crowdfunding refers to raising money from a large number of people who each contribute a relatively small amount. This is typically done via online crowdfunding platforms.
Early Traction/Series A Stage
This is the stage where your startup’s products or services have been launched in the market. Key performance indicators such as customer base, revenue, app downloads, etc. become important at this stage. Funds are raised at this stage to further grow user base, product offerings, expand to new geographies, etc. Common funding sources utilized by startups in this stage are:
- Venture Capital Funds: Venture capital (VC) funds are professionally managed investment funds that invest exclusively in high-growth startups. Each VC fund has its own investment thesis – preferred sectors, stage of startup, and funding amount – which should align with your startup. VCs take startup equity in return for their investments and actively engage in mentorship of their investee startups.
- Banks/NBFCs: Formal debt can be raised from banks and NBFCs at this stage as the startup can show market traction and revenue to validate their ability to finance interest payment obligations. This is especially applicable for working capital. Some entrepreneurs might prefer debt over equity as they debt funding does not dilute equity stake
- Venture Debt Funds: Venture Debt funds are private investment funds that invest money in startups primarily in the form of debt. Debt funds typically invest along with an angel or VC round.
- TReDs: To decrease the financing concerns faced by MSMEs in India, RBI introduced the concept of TReDS in 2014, an institutional mechanism for financing trade receivables on a secure digital platform. Trade Receivable Exchanges such as M1xchange, standardizes the process of funding MSMEs via Invoice Discounting. TReDS addresses the gaps in MSME industry as enterprises face challenges in getting their payments on time, thus creating working capital discrepancies. TReDS is a timely and effective solution to drive the MSME sector to the next phase of Indian economy.
Scaling/Series B & Above Stage
At this stage, the startup is experiencing fast rate of market growth and increasing revenues. Common funding sources utilized by startups in this stage are:
- Venture Capital Funds: VC funds with larger ticket size in their investment thesis provide funding for late stage startups. It is recommended to approach these funds only after the startup has generated significant market traction. A pool of VCs may come together and fund a startup as well.
- Private Equity/Investment Firms: Private equity/Investment firms generally do not fund startups however, lately some private equity and investment firms have been providing funds for fast-growing late-stage startups who have maintained a consistent growth record.
Initial Public Offering
Initial Public Offer (IPO) refers to the event where a startup lists on stock market for the first time. Since the public listing process is elaborate and replete with statutory formalities, it is generally undertaken by startups with an impressive track record of profits and who are growing at a steady pace. One of the benefits of an IPO is that a public listing at times can increase the credibility of the startup and be a good exit opportunity for stakeholders.
Any Angel investor, VC, or PE fund may buy out investors of a previous round to get their equity share as well. Also, there are various State Policies also which help the startups in various phases of funding or give them incentives and allowances to help them grow such as:
Startup India – State Policies
There are various initiatives by the respective states that are taken to help accelerate the growth of startups in various states. They proactively work towards helping the startups and the entrepreneurs in their ventures by giving them relaxation in building Angel Network, State funded grants, Matching Loans, Success Fee for fundraising. Various initiatives have been taken by States like Karnataka for setting up Idea2POC and Rajasthan for setting up Istart etc.
The following are some initiatives by the states:
- Karnataka: Government of Karnataka provides seed funding under the ‘Idea2PoC’ scheme of Startup Policy of Karnataka 2015-20. Idea2POC is given in the form of Grant-in-aid but limited to a one-time grant of up to INR 50 lakhs. Aspiring entrepreneurs can apply for the scheme incentive during call for proposal through an online portal. The website also mentions the required eligibility criteria.
- Gujarat: State Government provides seed funding to startups in the form of Sustenance Allowance, Product Development Assistance and Marketing Assistance. An amount of INR 10 Lacs is provided as seed funding
- Jammu and Kashmir: Government of J&K has launched Seed Capital Fund Scheme under which Seed Money up to maximum INR 10 Lacs the project cost is provided to eligible prospective entrepreneurs to kickstart their ventures
- Rajasthan: Government of Rajasthan provides seed funding in form of monthly sustenance allowance under the ‘Assistance for Startup at Idea or prototype stage’ of Rajasthan Startup Policy 2015. All eligible startups can apply for seed funding through their i Start Startup dashboard
4. How to Raise Equity Funding?
The entrepreneur must be willing to put in the effort and have the patience that a successful fund-raising round requires. The fund-raising process can be broken down into the following steps:
Assessing Need for Funding:
The startup needs to assess why the funding is required, and the right amount to be raised. The startup should develop a milestone-based plan with clear timelines regarding what the startup wishes to do in the next 2, 4, and 10 years. A financial forecast is a carefully constructed projection of company development over a given time period, taking into consideration projected sales data, as well as market and economic indicators. The cost of Production, Prototype Development, Research, Manufacturing etc should be planned well. Basis this, the startup can decide what the next round of investment will be for.
Assessing Investment Readiness:
While it is important to identify your requirement of funding, it is also equally important to understand if your startup is ready to raise funds. Any investor will take you seriously if they are convinced about your revenue projections and their returns. Investors are generally looking for the following in potential investee startups:
- Revenue growth and market position
- Favourable return on investment
- Time to break-even and profitability
- Uniqueness of the startup and competitive advantage
- The entrepreneurs’ vision and future plans
- Reliable, passionate, and talented team
Preparation of Pitchdeck:
A pitchdeck is a detailed presentation about the startup outlining all important aspects about the startup. Here is what you need to include in your pitchdeck
Investor Targeting:
To target the right set of investors, it is necessary to research their past investments in the market and speak with entrepreneurs who have successfully raised equity funding. This exercise will help you:
- Identify active investors
- Their sector preferences
- Geographic location
- Average ticket size of funding and
- Level of engagement and mentorship provided to investee startups
- Pitching events offer a good opportunity to interact with potential investors in-person. Pitchdecks can be shared with Angel Networks and VCs on their contact email IDs. Response time can be easily more than a month – rejection communication is not typically shared.
Due Diligence by Interested Investors
Angel networks and VCs conduct a thorough due diligence of the startup before finalizing any equity deal. They look at the startup’s past financial decisions and the team’s credentials as well as background. This is done to ensure that the startup’s claims regarding the growth and market numbers can be verified as well as to ensure that the investor is able to identify any objectionable activities beforehand. If the due diligence is a success, the funding is finalized and completed on mutually agreeable terms.