Trademark Registration Process Flowchart
Comprehensive Guide: Trademark Registration Process Flowchart
Trademarks are crucial assets for businesses, providing legal protection for their brands. Understanding the trademark registration process is essential for securing exclusive rights and preventing unauthorized use. This guide presents a detailed flowchart along with FAQs to navigate the intricacies of trademark registration seamlessly.
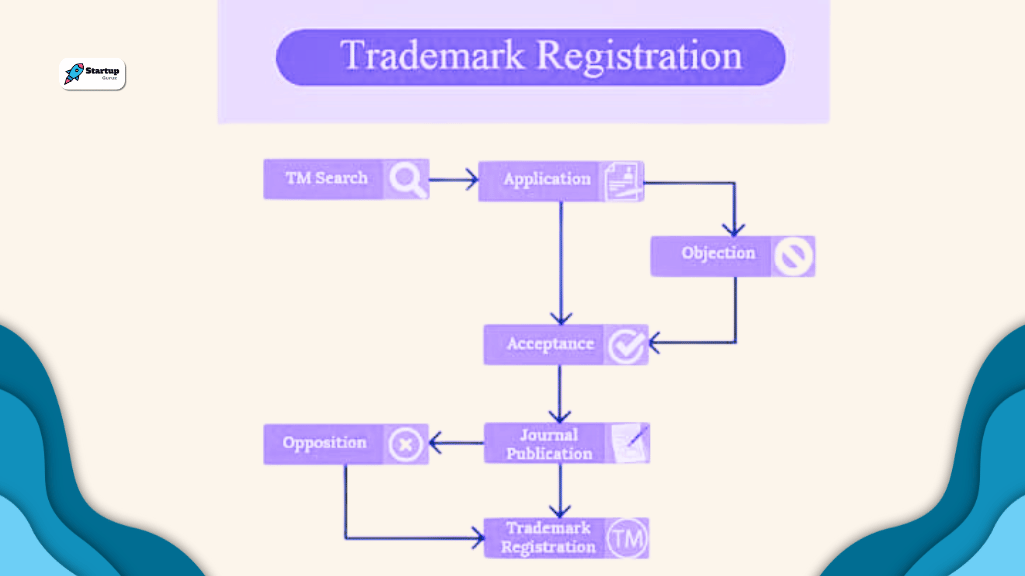
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Trademarks
- 1.1 Definition and Importance
- 1.2 Benefits of Trademark Registration
- 1.3 Types of Trademarks
- Trademark Registration Process Flowchart
- 2.1 Pre-application Considerations
- 2.2 Application Submission
- 2.3 Examination and Review
- 2.4 Publication for Opposition
- 2.5 Registration and Post-Registration
- FAQs on Trademark Registration Process
- 3.1 What is the significance of a trademark?
- 3.2 Why should I register my trademark?
- 3.3 What types of trademarks can be registered?
- 3.4 How long does the trademark registration process take?
- 3.5 What happens if my trademark application is opposed?
- 3.6 Can I use the ™ symbol before registration?
- 3.7 How do I enforce my trademark rights?
1. Introduction to Trademarks
1.1 Definition and Importance
A trademark is a distinctive symbol, word, or combination used to identify and distinguish goods or services. Trademark registration provides legal protection, preventing others from using similar marks.
1.2 Benefits of Trademark Registration
- Exclusive Rights: Sole ownership and the right to use the mark nationwide.
- Legal Protection: A basis for legal action against infringers.
- Brand Recognition: Builds trust and loyalty among consumers.
1.3 Types of Trademarks
- Word Marks: Standard characters without stylization.
- Design Marks: Logos or distinctive visual elements.
- Combined Marks: Combination of words and design.
- Service Marks: Identifying services rather than products.
2. Trademark Registration Process Flowchart
2.1 Pre-application Considerations
Step 1: Determine Trademark Eligibility
- Ensure the mark meets legal requirements.
- Avoid generic or descriptive terms.
Step 2: Conduct Trademark Search
- Check existing trademarks to avoid conflicts.
- Identify potential obstacles.
2.2 Application Submission
Step 3: Prepare Trademark Application
- Complete the application with accurate information.
- Specify the class of goods or services.
Step 4: Submit Application to Trademark Office
- File with the appropriate government authority.
- Pay the filing fee.
2.3 Examination and Review
Step 5: Trademark Office Examination
- Office examines the application for compliance.
- May issue office actions for corrections.
Step 6: Respond to Office Actions
- Address concerns raised by the trademark office.
- Amend application if required.
2.4 Publication for Opposition
Step 7: Publication in Trademark Gazette
- Notice of the application is published.
- Allows third parties to oppose.
Step 8: Opposition Period
- Interested parties can oppose the registration.
- Resolve opposition through negotiations or legal proceedings.
2.5 Registration and Post-Registration
Step 9: Registration
- If uncontested, the mark is registered.
- Certificate of registration is issued.
Step 10: Post-Registration Maintenance
- Renew the registration periodically.
- Enforce trademark rights against infringement.
3. FAQs on Trademark Registration Process
3.1 What is the significance of a trademark?
A trademark distinguishes your products or services, creating a unique brand identity. It provides legal protection and exclusivity in the market.
3.2 Why should I register my trademark?
Trademark registration grants exclusive rights and legal protection. It acts as a deterrent against infringement and strengthens your brand’s position in the market.
3.3 What types of trademarks can be registered?
Word marks, design marks, combined marks, and service marks are eligible for registration, provided they meet legal requirements.
3.4 How long does the trademark registration process take?
The duration varies but typically takes several months to a few years, depending on factors like office actions, oppositions, and processing times.
3.5 What happens if my trademark application is opposed?
If opposed, a legal proceeding may be initiated. Parties can negotiate a settlement or present their case before the trademark office.
3.6 Can I use the ™ symbol before registration?
Yes, you can use the ™ symbol to indicate your claim to the mark even before formal registration. It signals that you consider the mark as your trademark.
3.7 How do I enforce my trademark rights?
Enforce your rights by monitoring unauthorized use, sending cease and desist letters, and taking legal action if necessary. Registration strengthens your position in legal proceedings.
Conclusion
Navigating the trademark registration process is vital for safeguarding your brand identity. This comprehensive guide and flowchart, along with frequently asked questions, provide a roadmap to ensure a smooth journey from pre-application considerations to post-registration maintenance. By understanding the intricacies of trademark registration, businesses can secure their intellectual property rights and build a strong foundation for long-term success in the market.